The aged-care sector is experiencing a powerful digital transformation. Technology once seen as complex or unfamiliar is now becoming a trusted partner for older adults, care workers, and families. From telehealth consultations to wearable devices, smart home systems, and predictive analytics, innovation is reshaping how seniors stay healthy, connected, and independent.
This blog explores how digital tools are making aged care safer, more personalised, and more efficient, while still preserving the compassion and human connection that good care is built on.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Why Aged Care Needed a Digital Shift
- Telehealth: Changing the Doctor–Patient Relationship
- The Rise of Wearables and Health Devices
- Remote Monitoring in Aged Care (Main Focus)
- Smart Homes & Assistive Technologies
- Digital Platforms for Better Care Coordination
- Data Analytics & Predictive Care
- How Technology Benefits Care Workers
- Challenges & Ethical Considerations
- The Future of Technology in Aged Care
- Conclusion
Introduction
Aged care is undergoing one of the biggest shifts in its history. Technology—once considered optional—is now essential for supporting seniors with dignity, independence, and safety. For decades, providers relied on face-to-face interactions, manual documentation, and scheduled check-ins. While these remain vital, they don’t always meet the evolving needs of older adults or the increasing pressures on care workers.
Today, digital tools like telehealth, smart sensors, and wearable devices are creating a more responsive and proactive care ecosystem. One of the most impactful advancements is remote monitoring in aged care, enabling providers to detect risks early, respond quickly, and deliver more personalised care plans. This transformation is improving the quality of life for older adults while supporting the professionals who care for them.
Why Aged Care Needed a Digital Shift
1. Growing ageing population
People are living longer, increasing the demand for tailored, efficient care.
2. Workforce pressures
Care workers often manage heavy workloads and extensive documentation. Technology helps reduce administrative strain and enhance care quality.
3. Increasing health complexity
Chronic conditions like diabetes, dementia, and heart issues require consistent tracking. Tools such as remote monitoring in aged care make early intervention easier.
4. Desire for independence
Many older adults wish to live at home for as long as possible. Technology supports safe, independent living.
The goal of this shift isn’t to replace human care—it’s to strengthen it.
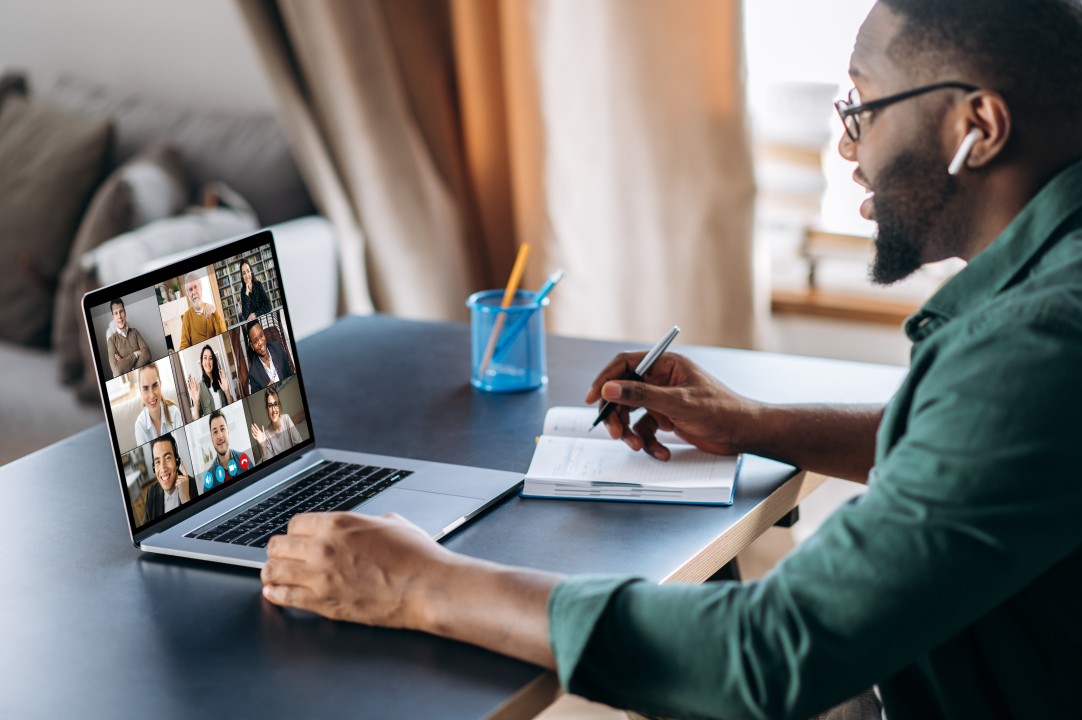
Telehealth: Changing the Doctor–Patient Relationship
Telehealth has become one of the most significant advancements in aged care. Seniors can consult with doctors, nurses, and specialists through video or phone calls without leaving their homes.
Benefits of Telehealth
- Reduces unnecessary hospital visits
Ideal for seniors with mobility or transport challenges. - Faster access to care
No long waiting times for appointments. - Lower exposure risks
Essential during flu seasons or outbreaks. - Better chronic disease management
Regular teleconsultations help track conditions like hypertension or COPD.
Telehealth integrates seamlessly with remote monitoring in aged care, as clinicians can view real-time data during consultations.
The Rise of Wearables and Health Devices
Wearable technology is now a lifeline for older adults, offering continuous support and insights.
Why Wearables Are Game-Changers
- Detect irregularities like abnormal heartbeat or low oxygen
- 24/7 fall detection
- Medication reminders
- Notifications for families
- Mobility tracking to identify changes in independence
When combined with remote monitoring in aged care, these tools provide vital information to care teams and support seniors living independently.
Remote Monitoring in Aged Care (Deep Dive)
Remote monitoring is one of the most transformative innovations in modern aged care. It involves devices, sensors, and software that continuously track a senior’s health and daily activities even when no caregiver is physically present.
Examples of Remote Monitoring Tools
- Smart sensors detecting movement, bathroom usage, or inactivity
- Wearables tracking heart rate, blood pressure, and sleep
- Fall detection and emergency alert systems
- Smart medication dispensers
- GPS devices for individuals with dementia
Why Remote Monitoring Matters
- Early detection saves lives
Sudden changes trigger instant alerts. - Supports ageing at home
Seniors can remain independent longer. - Improves chronic disease management
Conditions like diabetes or hypertension are easier to track. - Reduces hospital admissions
Early intervention prevents emergencies. - Provides family peace of mind
Real-time updates reduce anxiety and uncertainty.
Remote monitoring enhances safety without reducing human interaction—its purpose is to complement compassionate care.
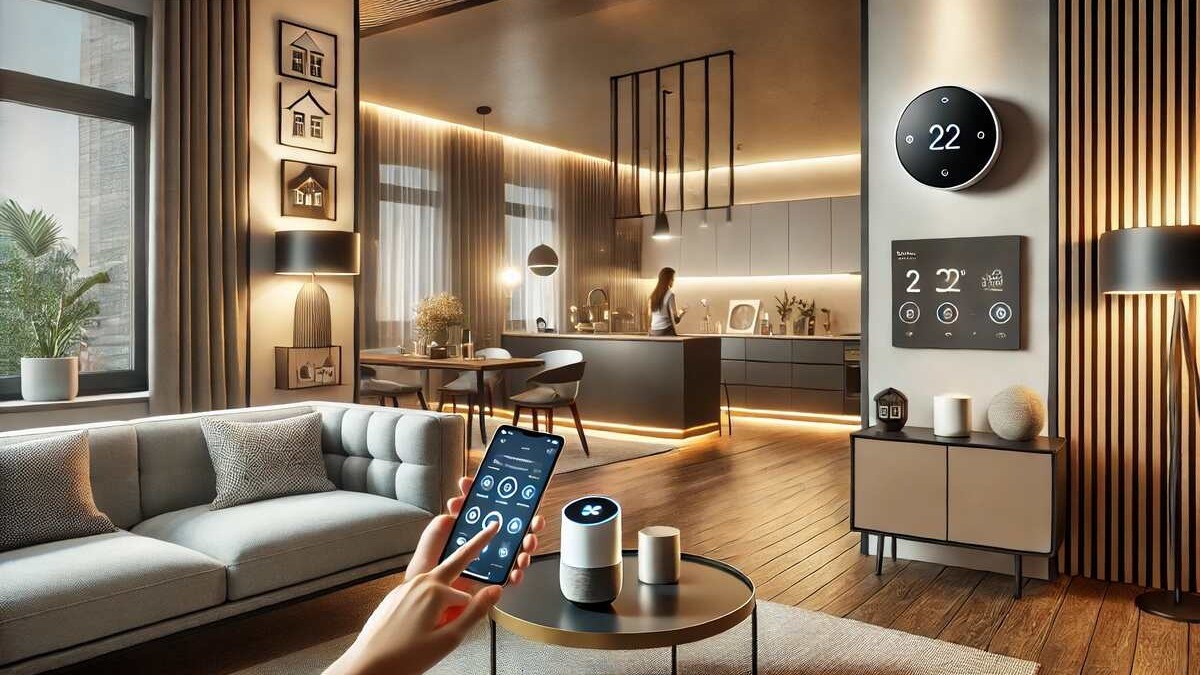
Smart Homes & Assistive Technologies
Smart home technology is making living spaces safer and more supportive for seniors.
Popular Smart Tools for Elderly Care
- Motion-activated lighting to prevent falls
- Voice assistants for reminders or emergency calls
- Smart stoves that automatically shut off
- Door and window sensors
- AI companionship devices to reduce loneliness
- Smart beds that detect sleep patterns
Integrated with remote monitoring in aged care, these tools create adaptive environments that respond to seniors’ needs.
Digital Platforms for Better Care Coordination
Digital care platforms centralise information and ensure seamless communication among care teams and families.
Key Features
- Progress notes
- Appointment and task tracking
- Medication charts
- Incident reporting
- Messaging tools
- Family portals
These platforms reduce paperwork, increase accuracy, and promote transparency.
Data Analytics & Predictive Care
Data is becoming a powerful tool in aged care.
Predictive analytics can identify:
- Fall risk increases
- Early signs of health deterioration
- Dementia progression
- Infection risk
- Behaviour changes
Combined with remote monitoring in aged care, predictive systems allow for proactive, tailored care plans that anticipate needs.
How Technology Benefits Care Workers
Technology is not only transforming senior care but also improving the daily work of professionals.
Benefits for Care Workers
- Less paperwork → more time with clients
- Real-time health data
- Safer working environments
- More accurate documentation
- Easier communication with healthcare teams
- Support in managing complex or chronic cases
Technology empowers care workers rather than replacing them.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite its advantages, technological adoption comes with challenges:
- Digital literacy gaps among seniors
- Privacy concerns, requiring consent and secure systems
- Cost barriers for some families
- Technology fatigue for care workers without proper training
Balancing innovation with empathy is essential for maintaining dignity.
The Future of Technology in Aged Care
The future of aged care is incredibly promising, with emerging technologies such as:
- AI-powered virtual nurses
- Robotic companions and mobility aids
- Smart clothing with built-in health sensors
- 3D-printed assistive devices
- Predictive analytics to prevent hospitalisation
- Fully integrated smart-home ecosystems
These innovations aim for more personalised, proactive, and empowering support.
Conclusion
Technology is rapidly reshaping aged care with positive and lasting impact. From telehealth to wearables and remote monitoring in aged care, digital tools help older adults stay safe, independent, and connected like never before.
But while innovation drives efficiency and safety, the heart of aged care remains the same: compassion, dignity, and genuine human connection. Technology enhances care—it never replaces it.